
Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD) that any sexually active person can get. Most people with the virus don’t have symptoms. Even without signs of the disease, herpes can still be spread to sex partners.
Genital herpes is an STD caused by two types of viruses. The viruses are called herpes simplex type 1 (HSV1) and herpes simplex type 2 (HSV-2).
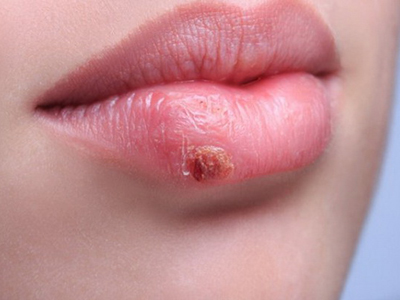
Oral herpes is usually caused by HSV-1 and can result in cold sores or fever blisters on or around the mouth. However, most people do not have any symptoms. Most people with oral herpes were infected during childhood or young adulthood from non-sexual contact with saliva.
Oral herpes caused by HSV-1 can be spread from the mouth to the genitals through oral sex. This is why some cases of genital herpes are caused by HSV-1.
Genital herpes is common in the United States. More than one out of every six people aged 14 to 49 years have genital herpes.
You can get genital herpes by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the disease. If you do not have herpes, you can get infected if you come into contact with the herpes virus in:
You can get herpes from a sex partner who does not have a visible sore or who may not know he or she is infected. It is also possible to get genital herpes if you receive oral sex from a sex partner who has oral herpes.
You will not get herpes from toilet seats, bedding, or swimming pools, or from touching objects around you such as silverware, soap, or towels. If you have additional questions about how herpes is spread, consider discussing your concerns with a healthcare provider.
The only way to avoid STDs is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex. If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting genital herpes:
Be aware that not all herpes sores occur in areas that are covered by a latex condom. Also, herpes virus can be released (shed) from areas of the skin that do not have a visible herpes sore. For these reasons, condoms may not fully protect you from getting herpes.
If you are in a relationship with a person known to have genital herpes, you can lower your risk of getting genital herpes if:
If you are pregnant and have genital herpes, it is very important for you to go to prenatal care visits. Tell your doctor if you have ever had symptoms of, or have been diagnosed with, genital herpes. Also tell your doctor if you have ever been exposed to genital herpes. There is some research that suggests that genital herpes infection may lead to miscarriage, or could make it more likely for you to deliver your baby too early.
Herpes infection can be passed from you to your unborn child before birth but is more commonly passed to your infant during delivery. This can lead to a potentially deadly infection in your baby (called neonatal herpes). It is important that you avoid getting herpes during pregnancy. If you are pregnant and have genital herpes, you may be offered anti-herpes medicine towards the end of your pregnancy. This medicine may reduce your risk of having signs or symptoms of genital herpes at the time of delivery. At the time of delivery, your doctor should carefully examine you for herpes sores. If you have herpes symptoms at delivery, a ‘C-section’ is usually performed.